Pension Basics
Next Topic
Why Pension?
Everyone will have an expectation that a time will come when they will be able to retire from the busy lifestyle and be worryfree even after they have no salary to depend on. The staff of Government entities have a pension plan which may be sufficient to provide a basic level of income. However, the majority of the workforce today, working in the Private sector do not have this facility and may have to accumulate a specific and sufficient corpus using private pension schemes.
Pensions are important for several reasons:
1. Steady Income: They provide a steady income during retirement, ensuring financial stability.
2. Longevity: With increasing life expectancies, pensions help your savings last throughout
retirement.
3. Rising Living Costs: Pensions can help you keep up with the rising cost of living and maintain
your standard of living in retirement.
4. Financial Independence: By investing regularly in your pension plan, you accumulate a considerable
sum, ensuring a financially independent life after retiring.
What is retirement planning:
The important aim of retirement planning is to have a secure and financially independent retired life.
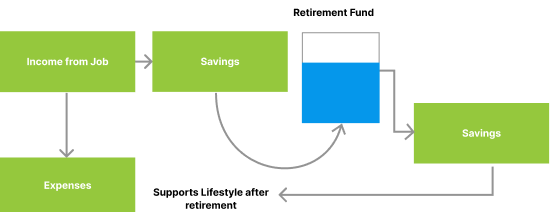
How is Pension different from Retirement Planning?
A Pension Plan or a Retirement Planning is one and the same
What is New or National Pension Scheme (NPS)?
“New Pension System OR the National Pension Scheme (NPS), helps in Retirement Savings/Planning and provides you with Tax benefits on investments. There are two types of NPS accounts (Tier 1 and Tier 2 schemes)
Difference between NPS and Old Pension Scheme (OPS) in India?
| Factors of Differentiation | Old Pension Scheme | New Pension Scheme |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Old Pension Scheme offers pensions to government employees on the basis of their last drawn salary | New Pension Scheme pays the employees for their investments in the NPS Scheme during their employment. The amount is invested in market-linked instruments. Employees make a monthly contribution at the rate of 10 % of their salary. A matching contribution is also made by the government. All citizens between 18 and 65 years are eligible for NPS. Private sector employees have also been given the opportunity to join NPS. |
| How much % do employees get? | 50% of the last drawn salary as a pension | 60% lumpsum after retirement and 40% to be invested in annuities for getting a monthly pension |
| Tax Benefits | No tax benefits | The employee can claim tax deductions of ₹1.5 lakh under Section 80C of income tax and up to ₹50,000 on other investments under 80CCD (1b) |
| Tax on Income | No tax benefits | 60% of the NPS Corpus is tax-free while the remaining 40% is taxable |
| Choice of Investing | No choice | Two choices: Active and Automatic |
| Who can avail? | Only government employees | Any Indian Citizen between 18-65 years. |
| Switching Schemes | OPS scheme can be switched to NPS | NPS scheme cannot be switched back to OPS in general, but central government employees can switch back to OPS in case of death and disablement of the employee. |
Schemes under the NPS are offered by nine pension fund managers mainly SBI, LIC, UTI, HDFC, ICICI, Kotak Mahindra, Aditya Birla, Tata, and Max. There are three asset classes or options G, C and E, which differ in terms of safety.
| Asset Class | Description |
|---|---|
| Government Securities (G) | Will only invest in Central and State government bonds. |
| Corporate Debt (C) | Fixed income securities of entities other than the government |
| Equities (E) | Investment in equity related products like index funds that replicate the Sensex. However, equity investment will be restricted to 50% of the portfolio. |
| Alternative Investment Funds (A) | Pooled investment funds which invest in venture capital, private equity,hedge funds, managed futures, etc. |
Is my pension and Pension Corpus Taxable?
Income from pension related investments, as on date is taxable
How to build your required Pension corpus? How much should you save for your retirement?
How to plan for retirement is a a process of determining retirement income goals and the actions necessary to achieve those goals. Here are the key components:
1. Identifying Income Sources: This could include pensions, investments, savings, or other income sources.
2. Estimating Expenses: Predicting your future living costs, healthcare expenses, and other needs.
3. Implementing a Savings Program: Regularly contributing to retirement accounts or other savings.
4. Asset Management and Risk Assessment: Ensuring your investments and savings are growing and are protected
against risks.
Retirement planning is not just about finances, but also about lifestyle choices such as how to spend time in retirement, where to live, and when to completely stop working. It’s recommended to start retirement planning as early as possible to ensure a secure and comfortable retirement.
Let’s assume you want to retire at the age of 55 and you expect to live till the age of 75 based on your anticipated life span. Your current expenses and inflation rate will represent your future monthly income (let’s say Rs.50,000 per month). This means you will need Rs. 6 lakhs per annum for a 20-year period, which means you need Rs.1.20 crores for your retirement. Now this is not sufficient. We have not taken in inflation in to account here.
If we assume inflation rate to be 7% per annum, the total corpus requirement works out to Rs.2.46 crores.
So if you need to accumulate this kind of money – you need the following: –
Time/Tenure: Save and invest early so you have more time to allow your money to grow
Being Systematic/Disciplined: Save and invest regularly to ensure your investments grow at a steady
rate
Growth: Invest in assets or investments that create value and beats inflation
What are other mandatory investments required along with building adequate Pension Corpus?
Ideally along with Retirement Corpus and Pension Investments , a customer should also have –
- Adequate Insurance coverage (Term and Health Insurance)
- Coverage for your Medical Expenses
- Pay off your major Debts if possible before Retirement
- Accumulate and Maintain contingency fund for your regular expenses
- Plan your major expenses and work to create a fund for the same – kid’s education/marriage, travel plans, buying a home etc.
Can a person have 2 or more pension plans?
Yes, an investor can subscribe to more than one (01) Pension Plan and achieve his Retirement corpus goals
How can an NRI/OCI subscribe to build their Pension Portfolio?
All Indians (Resident and Non Resident Indians) are eligible to subscribe to Pension Plans and Portfolio. As per Government of India requirements, it is suggested to have the following documents-
- Aadhar Card
- PAN Card
- Bank Accounts in India (NRE/NRO)
- Address Proof
Difference between Pension Plans and PPF investments?
Earlier Investors used the PPF as a tool to build a corpus for their retirement by putting aside sums of money regularly, over long periods of time (PPF has a 15-year maturity, and the facility to extend the tenure). However, the returns in PPF have been lower or less attractive in comparison to other Pension Plans.
How to choose a Pension plan
There are various Pension Plans based on Risk Profile and Investment appetite. Ideally Pension Plans fall under two (02) buckets -
- Safer Investment Instruments
- Investing in Financial Products which are comparatively riskier but gives higher returns in the long term.
The key is to Invest early and regularly to attain your Financial Corpus goals.
Transfer of ownership of Investment
Always maintain (assign) Nomination (Nominee) in full or percentage (%). In case of unforeseen events the investments will be distributed based on the assigned Nominations.
Pension Exit and Withdrawal?
A holder can exit and withdraw the amount that has been accumulated till that date, from a plan at any point in time. However, Ideally it is advisable to stay invested for the entire period required to achieve your Pension Corpus goal.


